On the Ballot - Ending Involuntary Servitude as Punishment for Crime
Five states have amendments removing constitutional language permitting involuntary servitude on midterm election ballot
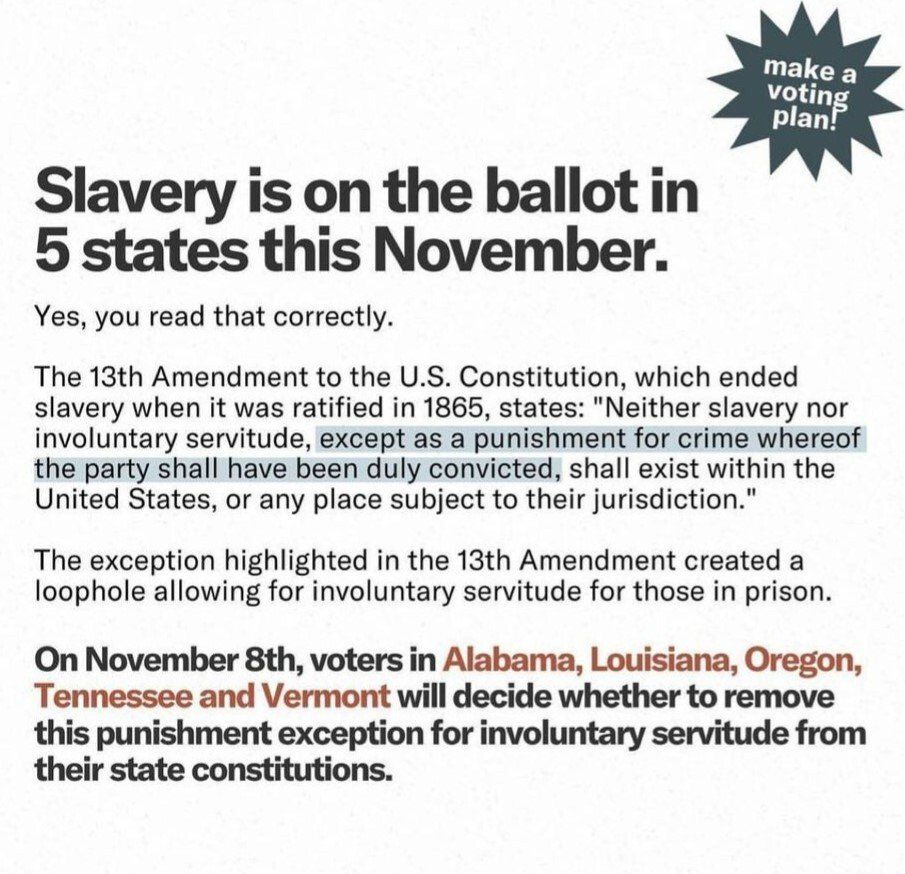
As of 2022, nine U.S. states included constitutional provisions permitting involuntary servitude, but not slavery, as a criminal punishment. Ten other states had constitutions that included provisions prohibiting enslavement and involuntary servitude but with an exception for criminal punishments. These constitutional provisions were added to state constitutions, in their original forms, from the 1850s to the 1890s. One state (Vermont) had a constitutional provision permitting involuntary servitude to pay a debt, damage, fine, or cost.
The five states and the corresponding amendments appearing on ballots for the November 8th 2022 midterm election:
- Louisiana: The measure is a constitutional amendment that would remove language from the state constitution that allows involuntary servitude as punishment for a crime. The amendment would also add language to say that the section of the constitution prohibiting slavery and involuntary servitude “does not apply to the otherwise lawful administration of criminal justice.”
- Tennessee: The measure removes language that allows the use of slavery and involuntary servitude as criminal punishments and replace it with the statement "Slavery and involuntary servitude are forever prohibited."
- Oregon: The measure repeals language from the state constitution that allows the use of slavery and involuntary servitude as criminal punishments and adds language that authorizes an Oregon court or a probation or parole agency to order alternatives to incarceration for a convicted individual as part of their sentencing.
- Vermont: The measure repeals language stating that persons could be held as servants, slaves, or apprentices with the person’s consent or “for the payments of debts, damages, fines, costs, or the like” and add “slavery and indentured servitude in any form are prohibited.”
- Alabama: The measure ratifies an updated and recompiled state constitution that was drafted to remove language considered racist, among other changes. The section stating "That no form of slavery shall exist in this state; and there shall not be any involuntary servitude, other than for the punishment of crime, of which the party shall have been duly convicted" would be removed.
Most recently in 2020, Utah and Nebraska voters decided to remove language from their respective constitutions that allowed the use of slavery and involuntary servitude as criminal punishments. Nebraska Amendment 1 was approved by a margin of 68.23% to 31.77%. Utah Constitutional Amendment C was approved by a margin of 80.48% to 19.52%.
To view the list of states that have ratified provisions addressing involuntary servitude in state constitutions since 2018, read this PDF document compiled by the Alabama Legislative Services Agency here (Note - this is a 2021 document and was not updated to include the above 5 proposed amendments).