Climate Warming Spells Catastrophe for US Jails & Prisons
“Dangerous heat impacting incarcerated people has been largely ignored, in part due to perceptions that their physical suffering is justified."
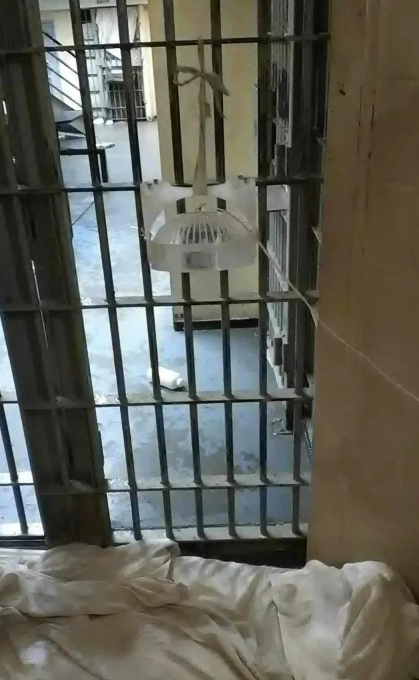

An estimated 1.8 million incarcerated people in the United States have been recently exposed to a dangerous combination of heat and humidity, and on average, experience 100 days of these conditions each year, with the majority of them in the 44 states that do not provide universal air conditioning to inmates. Tracking with climate change, in recent decades, the number of dangerous humid heat days in carceral facilities has increased, with those in the south experiencing the most rapid warming.
“Exposure to excess heat and humidity can lead to deadly heat stroke and kidney disease from chronic dehydration, among other health issues, for incarcerated people in the United States,” says Cascade Tuholske PhD, assistant professor of Human-Environment Geography at Montana State University, and first author of the report Hazardous heat exposure among incarcerated people in the United States. “The majority of these exposures are happening in state-run prisons and jails in Southern states that do not legally mandate access to air conditioning for the incarcerated. It is concerning because climate change is amplifying dangerous heat extremes in these locations.”
“Dangerous heat impacting incarcerated people has been largely ignored, in part due to perceptions that their physical suffering is justified,” says senior author Robbie Parks, PhD, assistant professor of Environmental Health Sciences at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. “Laws mandating safe temperature ranges, enhanced social and physical infrastructure, and focused health system interventions could mitigate the problem. Doing so is critical for incarcerated people, who have severely limited social and political agency.”
Incarcerated people are disproportionately susceptible to dangerous humid heat given preexisting health conditions. In fact, 43 percent of the state prison population has a previous mental health diagnosis, and people on psychotropic medications are at increased risk for heat illness.
Recent findings include:
- More than half of all dangerous heat and humidity exposures in the U.S. took place in Florida and Texas. The estimated 145,240 people in Texas and 98,941 in Florida housed in state-run carceral facilities in 2018—together 12 percent of all incarcerated people in the U.S.—accounted for 52 percent of exposure (28 percent in TX, 24 percent in FL).
- The worst facilities experienced dangerous heat and humidity between one-fifth and one-third of the year. An estimated 118 carceral facilities—largely in southern California, Arizona, Texas, and inland Florida—experienced, on average, 75 days or more per year of dangerous humid heat. The Starr County Jail in Rio Grande Texas that incarcerated an estimated 249 people in 2018 experienced the largest number of dangerous humid heat days, on average, during 2016 to 2020: 126.2 days per year.
- Areas with jails and prisons experienced 5.5 more dangerous humid heat days annually compared to other locations without carceral facilities. Carceral facilities in Arizona experienced 13.1 more days per year than the rest of the state and 40.9 more days compared to the entire continental U.S. during 1982-2020, on average. Carceral facilities are often built in areas with greater heat and humidity.
- Nearly a million incarcerated people are housed in facilities seeing an increase in dangerous humidity and heat. An estimated 915,627 people in the U.S.—45 percent of the estimated total incarcerated population—were housed in 1,739 carceral facilities with an annual increase in the number of dangerous days. Carceral facilities in Florida experienced, on average, 22.1 more days in 2020 compared to 1982, the greatest increase in dangerous humid heat days for all continental states.
The Safer Prisons, Safer Communities campaign is highlighting a nationwide crisis through overcrowding, understaffing and deteriorating conditions that make prisons unconducive to rehabilitation and create poor conditions for incarcerated people, prison staff, families and communities. You can read more about the campaign using this fact sheet.